
Click here to read this article in Marathi:ऑटिझम स्पेक्ट्रम डिसऑर्डर
Podcast on Autism Spectrum Disorder on TV Asia which was aired on April 7th, 2024!
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a complex developmental condition that involves persistent challenges in social interaction, speech and nonverbal communication, and restricted/repetitive behaviors.
The effects of ASD and the severity of symptoms are different in each person. No two children appear or behave the same way. Symptoms can range from mild to severe and often change over time. That’s why it is considered as a spectrum.
- The first case of autism was diagnosed in 1943.
- Early psychologists hypothesized that children became autistic due to “cold and unnurturing” mothers (Refrigerator mother theory). This theory was proven false in 1979. It is not caused by bad parenting.
- Autism spectrum disorder is four times more common in boys than in girls.
- Girls with ASD exhibit less obvious signs compared to boys.
- ASD1 is usually first diagnosed in childhood, usually around 2-3 years old.
- But some children develop normally until toddlerhood and then lose previously gained skills.
You might have heard about the conditions like autistic disorder, Asperger’s syndrome, pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified (PDD-NOS). But, since 2013, they are all called “autism spectrum disorders”.

According to the CDC (2020), one in 36 children is estimated to have autism in USA. More and more children are getting diagnosed with ASD. It could be due to changes with the diagnostic criteria as well as growing awareness about the condition. In 2006, the American Academy of Pediatrics recommended screening all children for autism during routine pediatrician visits at 18 and 24 months of age. This move may have led to diagnoses for children who would otherwise have slipped under the radar. However, a true increase in the number of people with an ASD cannot be ruled out.
![]()
Autism is a lifelong condition. However, many children diagnosed with ASD go on to live independent, productive, and fulfilling lives.
What causes ASD?2
Research suggests that autism develops from a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Genetic factors: Studies have shown that ASD runs in the family. Changes in certain genes increase the risk that a child will develop autism. If a parent carries one or more of these gene changes, they may get passed to a child, even if the parent does not have autism. These genetic changes can also arise spontaneously in an early embryo. These gene changes simply increase risk for the disorder.
Environmental factors: Certain environmental factors further increase the autism risk in people who are genetically predisposed to the disorder.
- Father’s age >40
- Mother’s age either teenage or >30
- Wide gap between parent’s ages
- Exposure to medicines, drugs, alcohol, smoking, pesticides during pregnancy
- Folic acid deficiency during pregnancy
- Viral or bacterial infections during pregnancy
- GDM (gestational diabetes mellitus) is associated with two-fold increased risk
- Maternal stress during pregnancy is associated with increased risk
- Premature birth, low birth weight, difficult labor causing oxygen deprivation to brain
- lead, mercury (fish consumption, cosmetics and dental amalgams), viral infections after birth
- Measles, Mumps, and Rubella (MMR) vaccination or any vaccines do not increase the risk of ASD!
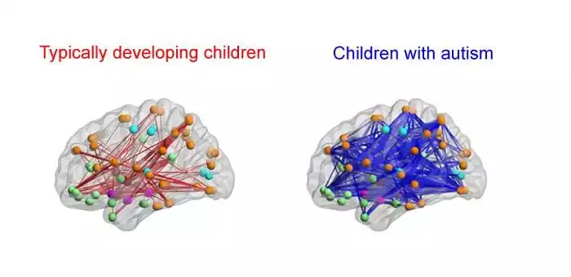
These genetic and environmental factors influence early brain development affecting how nerve cells (neurons) communicate with each other. It is also thought that, brain does not get customized properly and remains hyperconnected (unwanted connections do not go away).
How is ASD diagnosed?3
ASD is a clinical diagnosis.
There is no medical test (like blood test) or brain scans (like CT scan or MRI) or EEG (brain wave test).
Diagnosing ASD can be difficult. It is diagnosed based on observing how the child talks and acts in comparison to other children of the same age. Trained professionals typically diagnose autism by talking with the child and asking questions of parents and other caregivers.
Characteristics of autism spectrum disorder fall into two categories.
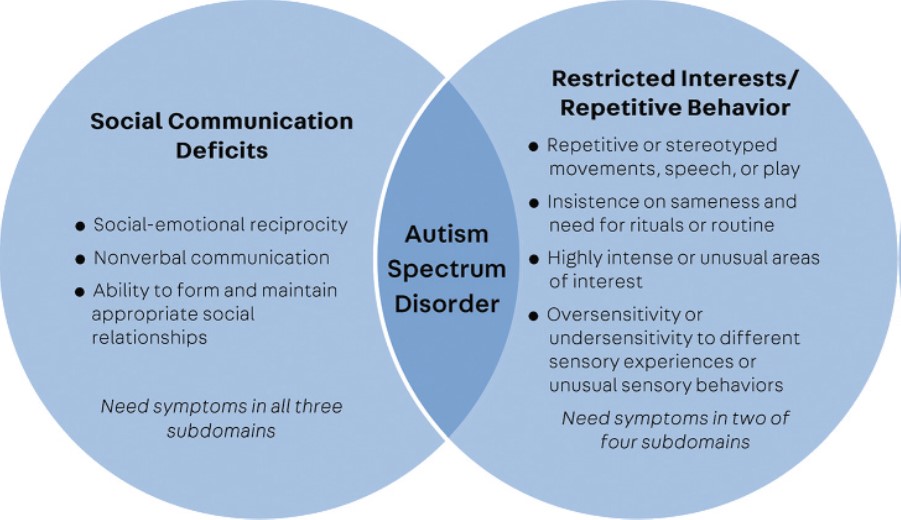
Social interaction and communication problems:
- Difficulties in normal back-and-forth conversation
- Reduced sharing of interests or emotions
- Poor or fleeting eye contact
- No pointing
- Difficulty making friends
- Challenges in understanding or responding to social cues and facial expressions
- Lack of awareness of the existence or feelings of others
- Aloof and distant from others
- Echolalia, sometimes called parroting, is defined as the repetition of someone else’s speech
- May use screaming, crying, tantrums, aggression or self-abuse as ways to communicate
- Laughing, crying, or showing distress for reasons not apparent to others
Restricted and repetitive patterns of behaviors, interests or activities:
- Repetitive movements such as hand flapping, finger flicking, rocking, grimacing or eye gazing
- Lining up toys
- Toe walking
- Speaking in a unique way (such as “scripting” from favorite shows)
- Insistence on routines, for example, they might need to eat particular foods in a specific order, or to take the same route from one place to another – every time. If these habits get disrupted, the child gets upset.
- Sensory processing issues such as indifference to pain/temperature, excessive smelling/touching of objects, fascination with lights and movement, being overwhelmed with loud noises (covering ears), etc
Many people with ASD have normal intelligence, but many others have mild or significant intellectual delays.
Additionally, people with ASD are at greater risk for some medical conditions such as sleep problems, seizures and mental illnesses. Some people with autism also have digestive problems, such as constipation, abdominal (belly) pain, or vomiting. Some research suggests that digestive problems occur more often in people with autism than in people without autism, but research is still being done on this topic.
How is autism treated?
- Early intervention with therapies is the key.
- Therapies like speech therapy, occupational therapy, physical therapy, behavioral therapy, ABA (applied behavioral analysis) therapy, sensory integration therapy are used to improve speech/communication skills, self-help skills, gross & fine motor skills, social skills.
- Animal assisted therapies like Hippotherapy (horse riding therapy), dog or dolphin assisted therapy.

- Music therapy: uses the elements of music to let people express their feelings and communicate.
- Massage therapy.
- The Picture Exchange Communication System (PECS) is an alternative Communication that uses visual symbols (pictures) to communicate with parents, teachers and peers. It does not require complex or expensive materials and can easily be used in school, home or in the community. It is particularly useful for children who are non-verbal and have limited or unclear speech. Speech therapist can help child to learn how to use PECS. With advanced technology, now, there are apps as well as speech generating devices which can be used in place of PECS cards/charts.

- A small study showed that children with ASDs who took fish oil supplements for six months reported improved cognitive and motor skills, concentration, eye contact, sociability, and sleep, as well as reduced hyperactivity and aggression. Click here to read more: Do I Need Fish Oil?
- Camel milk4 could play an important role in decreasing oxidative stress and improvement of autistic behavior. A larger scale study considering the period and dosage of camel milk is needed to determine the effect of camel milk on oxidative stress biomarkers and hence the treatment of ASD.
- Numerous studies support the role of probiotics in treating ASD. Probiotics can be obtained via either fermented food sources (kimchi, yogurt, cheese, Indian foods like idli, dosa, dhokla, curd, buttermilk, paneer) or over the counter supplements.
There is NO scientific evidence for:
- Chelation (a treatment to remove heavy metals such as lead from the body) therapy for heavy metals. A review of studies on chelation found some evidence of harm and no evidence of effectiveness.
- HBOT (hyperbaric oxygen therapy)
- Stem cell therapy (has been proposed, but has not tested)-As of Dec 19th, 2022, study shows that stem cell therapy is not recommended due to inadequate scientific evidence.
- Special diets like Gluten free diet or Casein free diet
- Vitamin B 12 injections
There is no medicine to cure autism. But, medicines can be used in certain conditions like seizures/epilepsy, sleep problems, aggression, ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder), mood disorders, anxiety etc. Medications used are Risperdal, Abilify, Clonidine, ADHD medications and melatonin.
Early diagnosis and treatment are important to reducing the symptoms of ASD and improving the quality of life for people with autism and their families. Having a child with autism affects the whole family. It can be stressful, time-consuming and expensive. Paying attention to the physical and emotional health of the whole family is important.
Autistic people possess a unique set of skills and perspectives. Hence, they are just differently abled, not disabled. They see the world differently than normal people.
Famous autistic people: Although autism can create challenges and difficulties with everyday life, it can also be seen as a gift which enables people to share amazing talents with the world around them. To name a few:
- Bill Gates – Co-founder of the Microsoft Corporation
- Temple Grandin – Animal Scientist
- Steve Jobs – Former CEO of Apple
- Elon Musk- Founder of Tesla
- Satoshi Tajiri- creator of Pokémon and the list goes on!
World Autism Awareness Day is an internationally recognized day on April 2 every year!

To increase the awareness and acceptance of ASD, children’s television program Sesame Street has introduced Julia, the fictional character.

There are few Hollywood and Bollywood movies based on ASD:

Tips for Parents:
- Learn as much as possible about autism spectrum disorder
- If you see any red flags, bring your child to a specialist who can evaluate your child and diagnose him/her
- Early diagnosis opens the doors for proper resources and early intervention brings best results
- Do not blame yourself for child’s diagnosis/behaviors
- Provide consistent structure and routine
- Connect with other parents of children with autism
- Seek professional help for specific concerns
- Take time for yourself and other family members
References:
- 1.https://www.psychiatry.org/patients-families/autism/what-is-autism-spectrum-disorder
- 2. https://www.autismspeaks.org/what-causes-autism
- 3. https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/autism/screening.
- 4. https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ecam/2013/602834/

I love the way you write any of the article aunty..you hold the audience till end without getting bored of reading info😎
Each of the information is clear and simple to understand by anyone 🤩
Thanks for spreading awareness🙏🙏
Thank you for the nice words, dear!
Thank you for the information madam.. god bless you for your good heart towards the children..
Thank you, dear!
Well written information, thanks Dr.Savitra
Thank you!
Very nice and informative article, Aunty.
Thank you, Komal 🙂