
To read this article in Marathi, click here: ओमेगा-3 फिश ऑइल
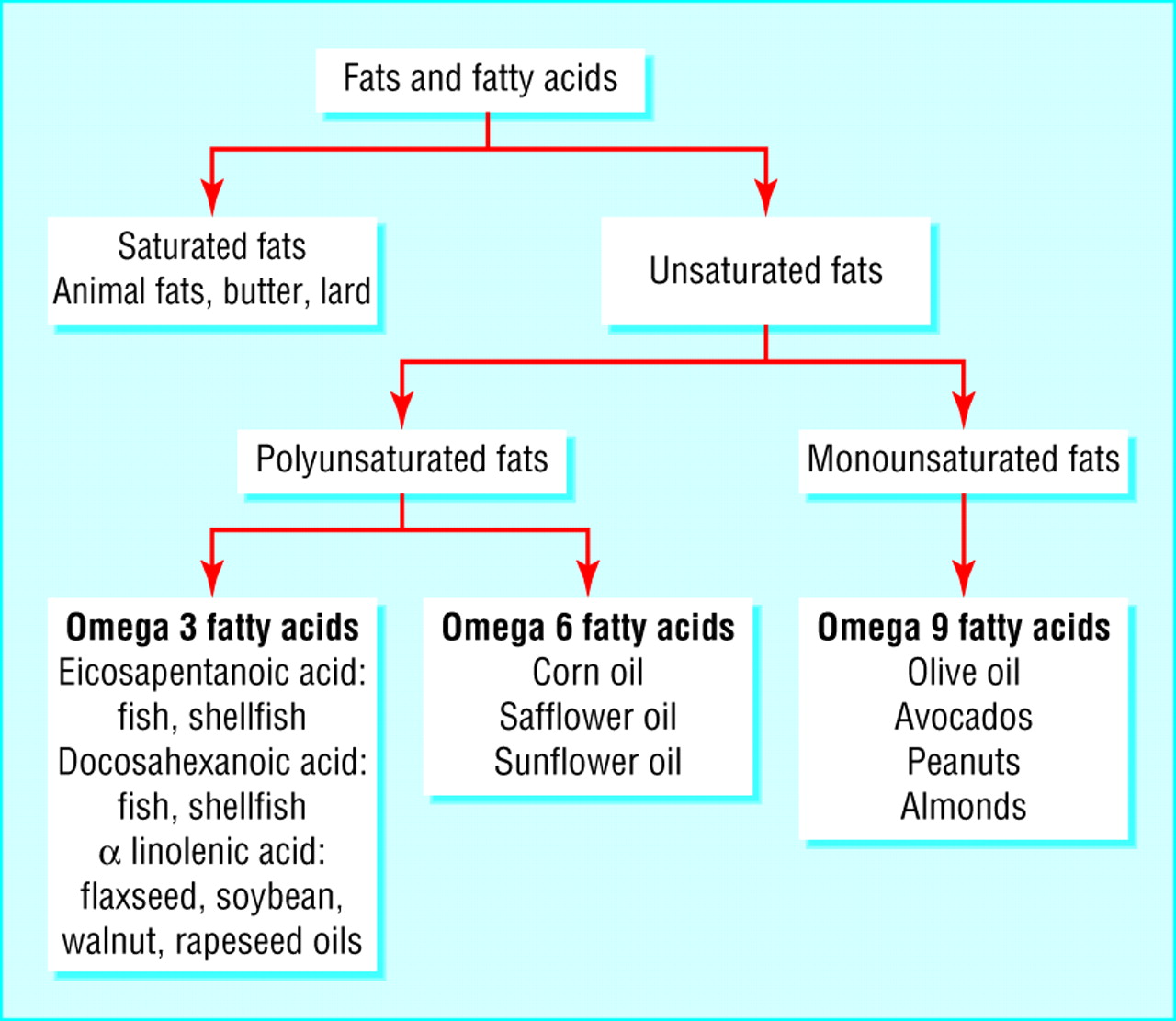
Carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals are basic components of our diet. The fats are made of fatty acids. There are two types of fatty acids: saturated and unsaturated.
Unsaturated fats are healthy fats.
They can be monounsaturated (omega 9 fatty acids) and polyunsaturated (omega 3 and 6). Human body can not make omega 3 fatty acids and hence they are called “essential fats”. Omega-6 fatty acids are also essential, so you need to obtain them from your diet.
In contrast to omega-3s and omega-6s, omega-9 fatty acids can be made in the body.
 The best sources of omega-3s are oily fish, whereas omega-6s and omega-9s are present in plant oils, nuts, and seeds. You can easily obtain omega-3, -6, and -9 fatty acids from your diet, but you need the right balance of each. The suitable proportion – omega 3:6:9 is 2:1:1. People who do not get enough omega-3 from their diet may benefit from an omega-3 supplement rather than a combined omega-3-6-9 supplement.
The best sources of omega-3s are oily fish, whereas omega-6s and omega-9s are present in plant oils, nuts, and seeds. You can easily obtain omega-3, -6, and -9 fatty acids from your diet, but you need the right balance of each. The suitable proportion – omega 3:6:9 is 2:1:1. People who do not get enough omega-3 from their diet may benefit from an omega-3 supplement rather than a combined omega-3-6-9 supplement.
Based on chemical size and shape, omega 3 fatty acids are of many types. The three most common ones are:
- Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)- EPA and DHA are commonly found in cold-water fatty fish like salmon, herring, sardines, and mackerel.
- Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA)- is a plant form of omega-3. It’s found in flaxseed, chia seed, walnuts, and canola and soybean oils.
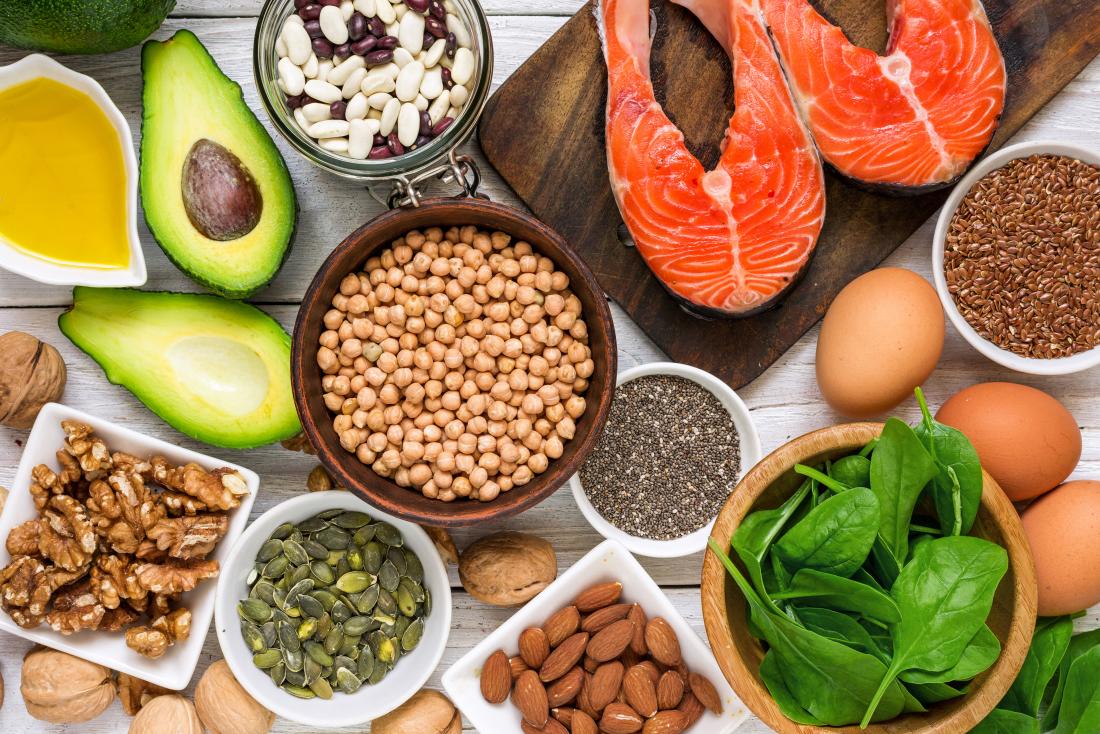
Omega-3s are found naturally in some foods and are added to some fortified foods. You can get adequate amounts of omega-3s by eating a variety of foods, including the following:
- Fish and other seafood (especially cold-water fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, tuna, herring, and sardines)
- Nuts and seeds (such as flaxseed, chia seeds, and walnuts)
- Plant oils (such as flaxseed oil, soybean oil, and canola oil)
- Fortified foods (such as certain brands of eggs, yogurt, juices, milk, soy beverages, and infant formulas)
 Omega-3 fatty acids are incredibly important.
Omega-3 fatty acids are incredibly important.
They have many powerful health benefits for your body and brain.
- To fight mental disorders: Bipolar disorder, Schizophrenia, anxiety and depression etc. Depression is one of the most common mental disorders. Studies indicate that people who consume omega 3s regularly are less likely to be depressed. The omega 3s supplements can improve their depression and anxiety symptoms.

- Can improve eye health: DHA is a major component of the retina of eye. Enough amount of omega-3 can reduce the risk of macular degeneration which is the leading cause of blindness.
- Can promote brain health during pregnancy and early life: Omega-3s are crucial for brain growth and development in infants. Getting enough omega-3s during pregnancy is associated with numerous benefits for the child:
-
-
- Higher intelligence
- Better communication and social skills
- Fewer behavioral problems
- Decreased risk of developmental delay
- Decreased risk of ADHD, autism and cerebral palsy
-
- ASD: Based on the available literature, omega-3 fatty acids can act as an effective supplement in individuals with autism.
- For heart health: Heart attacks and strokes are the world’s leading causes of death. The benefits of omega-3s are:
- Triglycerides: Omega-3s can cause a major reduction in triglycerides.
- Blood pressure: Omega-3s can reduce blood pressure levels in people with high blood pressure.
- “Good” HDL cholesterol: Omega-3s can raise “good” HDL cholesterol levels.
- Blood clots: Omega-3s can keep blood platelets from clumping together. This helps prevent the formation of harmful blood clots.
- Plaque: By keeping your arteries smooth and free from damage, omega-3s help prevent the plaque that can restrict and harden your arteries.
- Inflammation: Omega-3s reduce the production of some substances released during your body’s inflammatory response.

- Can reduce ADHD symptoms in children: Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a behavioral disorder characterized by inattention, hyperactivity and impulsivity. Several studies note that children with ADHD have lower blood levels of omega-3 fatty acids than their healthy peers. Recently, researchers observed that fish oil supplements were one of the most promising treatments for ADHD. Omega-3 supplements can improve attention and reduce hyperactivity, impulsiveness and aggression.

- Can reduce symptoms of Metabolic syndrome: Metabolic syndrome is a collection of following condition-
- central obesity (more belly fat)
- High BP (blood pressure)
- Insulin resistance
- High Triglycerides
- Low “good” HDL cholesterol
Omega-3 fatty acids can improve insulin resistance, inflammation and heart disease risk factors in people with metabolic syndrome.
- Fight inflammation: Inflammation is vital for our health. It is a natural response to infections. But sometimes it persists for long time and even without any infection. It is called as chronic inflammation and it is not good for our health. It can contribute to heart disease and cancer. Omega-3 can reduce the chronic inflammation.
- Fight Autoimmune disease: when your immune system mistakes healthy cells for foreign cells and starts attacking them, it is known as autoimmune diseases. Examples are: Type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis and Multiple sclerosis. Omega-3 fatty acids can help fight several autoimmune diseases.
- Can fight Alzheimer’s disease: As we age, our brain function declines. Omega-3 fats may help prevent age-related mental decline and Alzheimer’s disease, but more research is needed.
- Asthma in children: Omega-3 intake has been associated with a lower risk of asthma in both children and young adults.
- Fatty liver disease: Omega-3 fatty acids reduce liver fat in people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- For bone and joint health: Omega-3s may improve bone strength and joint health, potentially reducing your risk of osteoporosis and arthritis.
- Menstrual pain: Omega-3 fatty acids can reduce menstrual pain and may even be more effective than ibuprofen, an anti-inflammatory drug.
- Can improve sleep: Low levels of omega-3 fatty acids are associated with sleep problems in children and obstructive sleep apnea in adults. Low levels of DHA are also linked to lower levels of the hormone melatonin, which helps you fall asleep. Studies in both children and adults reveal that supplementing with omega-3 increases the length and quality of sleep.

- For skin: DHA is a structural component of your skin. Omega-3s can help keep your skin healthy, preventing premature aging, safeguarding against sun damage, reducing the risk of acne.
Getting omega-s fatty acids from whole foods, such as fatty fish two times per week, is the best way to ensure robust omega-3 intake. If you don’t eat fish, then you may want to consider taking an omega-3 supplement.
Fish oil is the fat or oil that’s extracted from fish tissue. It usually comes from oily fish, such as herring, tuna, anchovies, and mackerel. Sometimes, it is produced from the livers of other fish, such as cod liver oil. There are plant sources of omega-3s like Chia seeds, brussels sprouts, algal oil, hemp seed, walnuts, flaxseeds, perilla oil. It is important to note that the types of omega-3s found in fish oil have greater health benefits than the omega-3s found in some plant sources. Good EPA and DHA supplements include fish, krill, and algal oils. For vegetarians and vegans, taking a DHA supplement made from algae is recommended.
How much omega-3 you should take?
Various health organizations have different recommendations. The recommended dose of EPA+DHA is 250-500 mg daily to maintain the overall health. Higher amounts are recommended for certain health conditions. For reference, a typical 1,000-mg fish oil soft gel generally contains about 250 mg of combined EPA and DHA.
Too much omega 3 can be harmful: According to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), taking up to 2,000 mg of combined EPA and DHA per day from supplements is safe. Do not exceed 3,000 mg per day.
 The following are some side effects of high doses of omega 3 fish oil.
The following are some side effects of high doses of omega 3 fish oil.
- High blood sugar-taking 8000 mg of omega 3 fish oil can lead to increase in blood sugar level in people with diabetes type 2
- Bleeding: Taking large amounts of fish oil can inhibit blood clot formation, which may increase the risk of bleeding and cause symptoms such as nosebleeds or bleeding gums. Also, stop taking omega 3 fish oil 2-3 weeks before any surgery.
- Low BP: Fish oil is beneficial in lowering high blood pressure. Fish oil may also interact with blood pressure-lowering medications.
- Diarrhea: is a side effect of omega-3 fatty acid supplements such as fish oil and flaxseed oil.
- Acid reflux: Fish oil is high in fat and may cause acid reflux symptoms such as belching, nausea, indigestion and heartburn in some people.
- Stroke: high intake of omega-3 fatty acids could increase the risk of hemorrhagic stroke.
- Vitamin A toxicity: Certain types of omega-3 fatty acid supplements, such as cod liver oil, are high in vitamin A, which can be toxic in large amounts.
- Insomnia: Although moderate doses of fish oil have been shown to improve sleep quality, one case study suggests that taking large amounts caused insomnia.
References: http://1. https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/fish-oil

Very informative n clear cut as always🙏
Thank you 🙂