
Click here to read this article in Marathi: व्यायामाचे तंत्र
Physical activity is a key component of a healthy lifestyle. Being physically active is one of the most important activities that people of all ages can do to improve their health. It begins in infancy and extends to adulthood. Parents should emphasize physical activity, beginning early in a child’s life.
Only about one in five adults and teens get enough exercise to maintain good health. Nowadays, spending time in sedentary activities is increasingly common. Increased use of screens (TV, computers, smart phones etc) is reducing or eliminating physical activity. If you live a sedentary lifestyle, spending less time sitting is a great way to start becoming more active.
In the United States, the number of children and adults with obesity has continued to rise. Being underweight or overweight is not good. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is a lifestyle that includes healthy eating, regular physical activity, and balancing the calories you consume with the calories your body uses.
Body Mass Index (BMI) and waist circumference are screening tools to estimate weight status in relation to potential disease risk. However, BMI and waist circumference are not diagnostic tools for disease risks.
- For adults, your BMI (body mass index) should be between 18.5 to 25.
- You can check your BMI here: BMI Index Chart
- Maintain your waist circumference less than 40 inches for men and less than 35 inches for women. It is measured around the belly button.
- Children with obesity can be bullied and teased more than their normal weight peers. They are also more likely to suffer from social isolation, depression, and lower self-esteem. The bullying effects will follow them into adulthood.
- Children with obesity are at higher risk for having other chronic health conditions and diseases, such as heart disease, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, asthma, sleep apnea, bone and joint problems, and type 2 diabetes.
- Along with developing healthy eating habits, regular physical activities should be implemented (running, 20 jumping jacks, pushups)

Benefits of physical activity:
- Regular physical activity increases lean body mass, muscle, and bone strength and promotes physical health.
- It fosters psychological well-being
- It reduces the symptoms of anxiety and depression
- Increases self-esteem and capacity for learning
- Helps to handle the stress
- Helps attain/maintain healthy weight
- Reduces your risk of a heart attack
- Lowers blood cholesterol level
- Lowers the risk of type 2 diabetes
- Lowers blood pressure
- Lowers risk of developing osteoporosis (weak and brittle bones)
- Lower your risk of falls (in older adults)
- You will feel better– with more energy, a better mood, more relaxed.
- Exercising with others provides an opportunity for more social interaction
- Increased fitness may improve your sleep pattern
- Exercise increases the levels of chemicals in your brain, such as serotonin, endorphins (happy hormones).
- Improves cognitive function.
- Significantly lowers the risk of developing several commonly occurring cancers and lowers the risk of several other cancers in men and women:
- Bladder
- Breast
- Colon
- Endometrium
- Esophagus (adenocarcinoma)
- Kidney
- Lung
- Stomach
Aren’t you impressed by the huge list of benefits of doing regular physical activities? Let us learn more about physical activities.
There are mainly three types of activities:
1. Aerobic Activity: physical activity (also called as cardio) where the large muscles move in a rhythmic manner for a sustained period of time. Examples are:
- Jumping Jacks
- Jogging in Place
- Brisk walking
- Running
- Bicycling
- Jumping rope
- Swimming
Aerobic activity causes a person’s heart to beat faster, and they will breathe harder than normal. This improves heart function and increases stamina.
2. Muscle-Strengthening Activity: This kind of activity, which includes resistance training and weight lifting, causes the body’s muscles to work or hold against an applied force or weight. Examples are:
- Weight lifting
- Climbing a tree
- Doing push-ups or pull-up

3. Bone-Strengthening Activity: This kind of activity (sometimes called weight-bearing or weight-loading activity) produces a force on the bones of the body that promotes bone growth and strength. This force is commonly produced by impact with the ground. Examples of bone-strengthening activity include
- Jumping jacks
- Running
- Brisk walking
- Weight-lifting exercises
Bone-strengthening activities can also be aerobic and muscle strengthening.
How much physical activity is recommended for your age? The second edition of the Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans provides science-based guidance to help people ages 3 years and older improve their health through participation in regular physical activity.
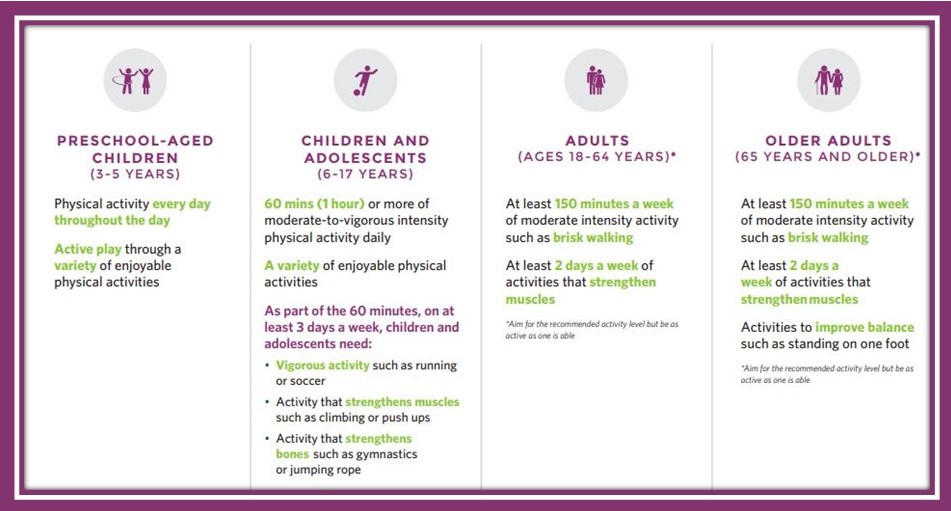
Some types of physical activity are better-suited for children than adolescents. For example, younger children usually strengthen their muscles when they do gymnastics, play on a jungle gym, or climb trees. Children do not usually need formal muscle-strengthening programs, such as lifting weights. As children grow older and become adolescents, they may start structured weight lifting programs.
Physical Activity Guidelines 1:
Infancy (birth–11 months)
• Infants should interact with caregivers in daily physical activities that are dedicated to exploring movement and the environment.
• Infants’ physical activity should promote skill development in movement.
Toddlers (1–3 years)
• Toddlers should engage in at least 60 minutes to several hours per day of unstructured physical activity. They should not be sedentary for >60 minutes
at a time except when sleeping.
• At least 30 minutes should be structured physical activity each day.
• Toddlers should be given ample opportunities to develop movement skills that will serve as the building blocks for motor skill and bone development.
Preschool aged children (3-5 years)
- Preschool-aged children should be physically active throughout the day for growth and development.
- Adult caregivers should encourage children to be active when they play—aiming for 3 hours a day—and limit their screen time.

School-Aged Children and Adolescents (6–17 years)
- Daily 60 minutes (1 hour) or more of aerobic physical activity including the following:
- muscle strengthening activities – 3 days each week, and
- bone strengthening activities – 3 days each week.




Adults (18 and above)
Adults should move more and sit less throughout the day. Some physical activity is better than none. Adults who sit less and do any amount of moderate-to-vigorous intensity physical activity gain some health benefits.
They need to do two types of physical activity each week –aerobic activity and muscle strengthening. The recommendation is 150 minutes each week. I know, it sounds like a lot of time. You can do 30 minutes a day, 5 days a week. You do not have to do it all at once. You can even break it up into smaller blocks during the day.

Older adults (65 years and older) can additionally do activities to improve balance such as standing on one foot.
Sun salutations or Surya Namaskar: The Sun Salutation or Surya Namaskar is a series of twelve yoga postures. There are many variations. Start with 5 or 6 repetitions and gradually build to 12 or more. All these postures are focused on different muscle groups and nerves.
Benefits of sun salutation:
- This helps you tone your body.
- It gives flexibility and improves body posture.
- If it is done in faster manner, it acts like cardio workout.
- It improves blood circulation.
- It helps to lower cholesterol levels.
- It improves digestion and helps to lose weight.
- It improves insulin sensitivity, hence helps in diabetes.
- It causes good hormonal balance.
The following are 12 yoga poses or asanas. Do not worry about difficult names of yoga postures. You will get better if you continue practicing it on daily basis. This is the amazing form of exercise and good enough to stay healthy. You can watch some YouTube videos to learn the postures correctly.
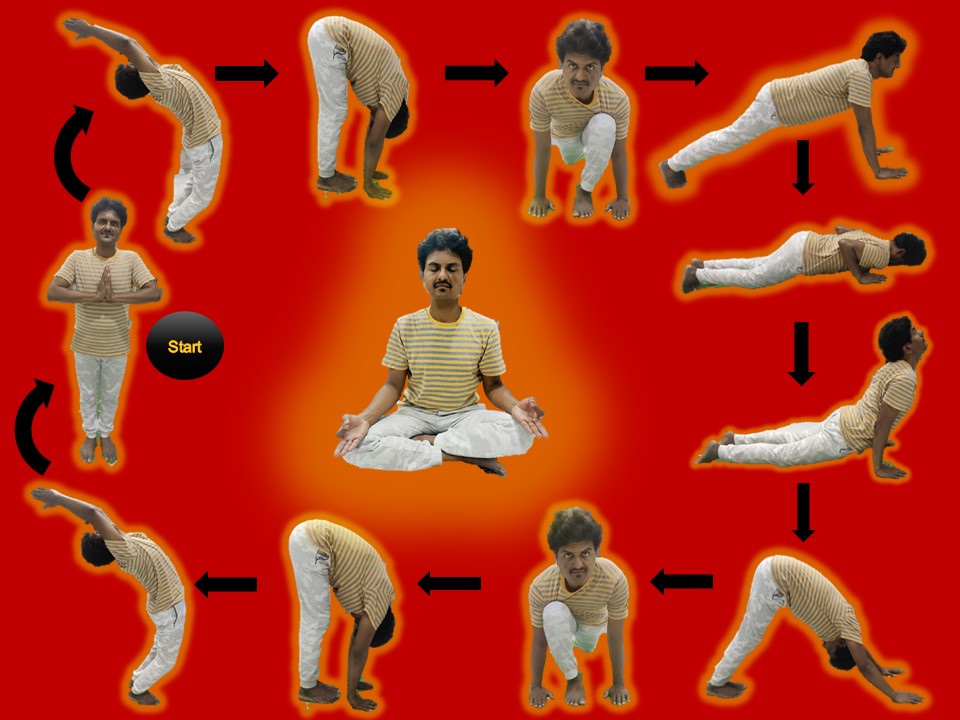

- Tadasana/Mountain pose: Stand with your feet apart. Hold hands in namaskara position. Take several breaths.
- Urdhva Hastasana/upward salute: Inhaling, stretch your arms up and arch back from the waist, legs straight.
- Uttanasana/Standing forward fold: Exhaling, fold forward and press palms down. Bend your knees if necessary.
- Ardha Uttanasana/Half standing forward fold: Inhaling, bring the left or right leg back and place the knee on the floor.
- Chaturanga Dandasana/Four-Limbed Staff Pose: Retaining the breath, bring the other leg back. Support your weight on toes and hands.
- Urdhva Mukha Svanasana/Upward-Facing Dog Pose: Exhaling, lower your knee, then chest and then forehead. Keep your hips up.
- Adho Mukha Svanasana/Downward-Facing Dog Pose: Inhaling, lower your hips, point your toes and bend back. Look up and back.
- Ardha Uttanasana/Half Standing Forward Fold: Exhaling, raise your hips and make your posture in an inverted “v” shape.
- Uttanasana/Standing forward fold: Inhaling, step forward and place the opposite foot (from position 4) between two hands, look up as in position 4.
- Urdhva Hastasana/Upward salute: Exhaling, bring the other leg forward and bend down from the waist, placing palms as in position 3.
- Uttanasana/Standing forward fold: Exhaling, fold forward and press palms down. Bend your knees if necessary.
- Tadasana/Mountain pose: Stand with your feet apart. Hold hands in namaskara position. Take several breaths.
Tips for parents to keep their children active 2: Parents can help shape their child’s attitudes and behaviors regarding physical activity. To implement it, first you have to know the recommendations. Encourage your child to be physically active for 60 minutes or more each day.
- Start early. Young children love to play and be active. Encouraging lots of safe and unstructured movement and play can help build a strong foundation for an active lifestyle.
- Set a positive example by leading an active lifestyle yourself.
- Make physical activity part of your family’s daily routine by taking family walks or playing active games together.
- Give your children equipment that encourages physical activity (e.g. bike, scooter, bouncing ball, etc)
- Take young people to outside places where they can be active, such as public parks, community baseball fields, or basketball courts.
- Be positive about the physical activities in which your child participates and encourage them to be interested in new activities.
- Make physical activity fun. Fun activities can be anything your child enjoys, either structured or non-structured. Activities can range from team or individual sports to recreational activities such as walking, running, skating, bicycling, swimming, playground activities, or free-time play.
- Instead of watching television after dinner, encourage your child to find fun activities to do on their own or with friends and family, such as walking, playing chase, or riding bikes.
- Be safe! Always provide protective equipment such as helmets, wrist pads, or knee pads for activities such as riding bicycles, or scooters, skateboarding, roller skating, rock-wall climbing, and other activities where there may be a high risk of injuries.
- Ensure also that activities are appropriate for the age of your child.
Take Home Message:
- Physical health is one of the major pillars of a healthy life.
- It begins in infancy and extends throughout adulthood.
- Make it a family project.
- It keeps you healthy, happy, stress-free, disease-free, and prolongs your life.
- The best time to start was yesterday, the second best time to start is today. It is never too late 🙂
- Some physical activity is better than none.
- If you are sedentary, start with sitting less. Try standing up/jumping jacks during the commercials or typing an email standing up.
- There are three types of physical activities:
- Aerobic
- Muscle strengthening and
- Bone strengthening
- Follow the age-appropriate recommendations and choose the activities which suit your need and lifestyle.
- Children have different recommendations based on their age.
- Adults should be physically active at least 150 minutes per week.
- For adults, BMI (body mass index) should be between 18.5 to 25.
- You can check your BMI here: BMI Index Chart
- Maintain your waist circumference less than 40 inches for men and less than 35 inches for women.
- Adopt a mindful diet to achieve a healthy weight.
- Be healthy and be happy!
References:
- 1. https://health.gov/our-work/physical-activity/current-guidelines
- 2. https://www.cdc.gov/physicalactivity/basics/adding-pa/activities-children.html
- Sun salutation GIF source: http://yogasite.com/sunsalute.htm

Nice, simple and informative.
Savi nehami pramane very informative write up keep it up .
VERY Informative …Very well written✍️👌✌️
Very informative should be included in school curriculum
V.nice yoga information, diet,exercises, BMI,all medically fit studies r v.nice…article is useful to all
Simple and encouraging!
Super! Well written!
Woow,savi…
Very informative..
As usual, Dr. Savitra you are a Blessed soul and have been sent with a purpose to Shower the Bliss 🕉🙏🏻
Very nice article Aunty
Thank you, Harish 🙂
Nice one..keep posting…
Thank you, Venu 🙂
Very nice and useful article for everybody in this present situation..tq very much for sharing
I am glad you liked it. Thank you, dear 🙂