The word CANCER can be very frightening to anyone. As knowledge and action are our best weapons in the fight against cancer, the first step is to have basic understanding about it. In this article, we will explore the fundamentals of cancer, its causes, common types, screening tests and potential prevention strategies.
Introduction: Tumor is an abnormal growth or mass of tissue. A tumor can be cancerous or benign. A benign tumor means the tumor can grow but will not spread. A cancerous tumor is malignant, meaning it can grow and spread to other parts of the body. Hippocrates, a Greek physician, used the term cancer because the growth looked like a “crab”.
Cancer is a complex and devastating disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a term used to describe a group of diseases characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells in the body.
What Causes Cancer?
Cancer is a multifactorial disease, meaning it can arise from a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Some common risk factors associated with cancer include:
- Genetic Factors: Certain inherited gene mutations can increase the risk of developing cancer.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to carcinogens, such as tobacco smoke, asbestos, certain chemicals, radiation, and pollutants, can increase the risk of developing cancer.
- Lifestyle Choices: Unhealthy lifestyle habits, including tobacco and alcohol use, poor diet, lack of physical activity, and excessive sun exposure, can contribute to the development of cancer.
Warning Signs of Cancer:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fever
- Fatigue (the feeling of extreme tiredness)
- Pain
- Skin changes (jaundice, excessive hair growth, darkening of skin, itching)
- Change In bowel habits or bladder function
- Unusual bleeding or discharge
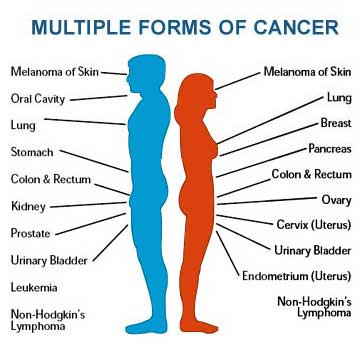
Common Types of Cancer:
There are numerous types of cancer that can affect different organs and tissues in the body. Each type of cancer has its own unique characteristics, risk factors, and treatment approaches. Regular screenings and early detection can significantly improve the chances of successful treatment and recovery.
Here are some of the different types of common cancers:
- Breast Cancer: common in women, but can also occur in men
- Lung Cancer
- Colorectal Cancer (including colon and rectal cancer)
- Prostate Cancer: one of the most common types of cancer in males
- Skin Cancer (including melanoma and non-melanoma types)
- Bladder Cancer
- Kidney Cancer (renal cell carcinoma)
- Leukemia (blood cancer)
- Lymphoma (including Hodgkin’s lymphoma and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma)
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
- Cervical Cancer
- Uterine (Endometrial) Cancer
- Liver Cancer
- Stomach (Gastric) Cancer
- Esophageal Cancer
- Testicular Cancer
- Thyroid Cancer
- Brain Tumors
- Bone Cancer
 Prevention and Early Detection: Remember, while these preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing cancer, they do not guarantee complete prevention.
Prevention and Early Detection: Remember, while these preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing cancer, they do not guarantee complete prevention.
Here are some essential strategies:
- Avoid tobacco, including smoking and chewing tobacco. Smoking is a significant risk factor for several types of cancer, including lung, mouth, throat, esophageal, and bladder cancer. If you are a smoker, quitting is the best thing you can do for your health.
- Limit alcohol consumption. If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation.
- Protect your skin from excessive sun exposure and use sunscreen regularly. Excessive exposure to the sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays increases the risk of skin cancer. Protect your skin by seeking shade, wearing protective clothing (long sleeves, wide-brimmed hats), and applying sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher whenever you are outside.
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit the consumption of processed foods, sugary snacks, and red meat. A diet rich in fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants can support your overall health and reduce the risk of cancer. Click here to read more: A Mindful Diet Include millet in your diet which are rich in antioxidants. Click here to read more: Millets: A Nutritious Ancient Grain
- Engage in regular physical activity to maintain a healthy weight. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week. Click here to read more: Dare to Be Fit
- Practice Safe Sex and Get Vaccinated. Certain types of cancer, such as cervical, anal, and some types of liver cancer, can be caused by viruses like human papillomavirus (HPV) and hepatitis B. Practice safe sex by using barrier methods, such as condoms, and consider getting vaccinated against HPV and hepatitis B to lower your risk.
- HPV vaccine: 2 doses (at 0 and 6 months) for ages 9 through 14 years and 3 doses (at 0, 1-2 months and 6 months) for ages 15 through 26 years can be given.
- The hepatitis B vaccine (3 doses at 0, 1-2 months and 4-6 months) is recommended for all ages <59 years and adults >60 years with risk factors for hepatitis B.
- Occupational and Environmental Hazards: Minimize exposure to harmful substances such as asbestos, benzene, industrial chemicals, and pollutants, as they can increase the risk of cancer. Follow safety protocols and use protective gear if you work in a potentially hazardous environment.
- Regular screenings can help detect certain cancers at an early stage when treatment is most effective. Follow the recommended guidelines for screenings such as mammograms, Pap smears, colonoscopies, and other age-specific screenings based on your gender and risk factors.

Screening Tests for Some Cancers: By investing an hour or two in knowing and understanding the available screening tests, and when to get them done, you may be able to add years to your life! Use your birthday as a reminder to get them done.
- Mammogram is an X-ray picture of the breast. Yearly mammogram starting at the age of 40 is recommended.
- Pap smear for cervical cancer: pap smear is a procedure to test for cervical cancer in women. It should begin at the age 21 years.
- Colonoscopy for Colo-rectal cancer: Colonoscopy every 10 years should begin at age 50.
Click here to read about recommended screening tests: Know Your Health Screening Checklist
Treatment Options:
Cancer treatment depends on the type, stage, and location of the cancer, as well as the individual’s overall health. Common treatment options include:
- Surgery: The removal of the tumor or affected tissue is often the first-line treatment for many solid tumors.
- Chemotherapy: This treatment involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from multiplying.
- Radiation Therapy: High-energy beams are directed at the cancerous cells to destroy them or prevent their growth.
- Immunotherapy: It helps your immune system to identify, fight and destroy cancer cells.
- Targeted Therapy: is a type of cancer treatment that targets the changes in cancer cells that help them grow, divide, and spread.
Conclusion: Cancer remains a complex and challenging disease. The advancements in research and medical technology continue to improve the outcomes for patients. It is essential to be aware of the risk factors, engage in regular screenings, and lead a healthy lifestyle to reduce the chances of developing cancer.

Dear Dr Savi again a great effort by you for a common man to make understand all about cancer !
Thank you, dear!
Commendable @savi
Thank you 🙂
Savi very nice article.
Thank you, dear!
Dr. Savitra Aunty, Thank-you for such a nice article, this helps to understand better about cancer.
Thank you, Yogesh!